CS144 Lab 1
Overview
在 Lab 0 中,我们使用 Linux 内置的 TCP 协议实现了一个简易的抓取网站信息的 socket ,即 webget 。之后,我们为 Internet 中的通信实现了一个可靠的 byte stream ,尽管 Internet 本身仅仅提供 「best-effort」 服务。
Getting Started
- 首先检查是否已经备份好了 Lab 0 的代码,因为在合并 Lab 1 的文件时可能会发生冲突导致丢失。
- 然后
git fetch获取最新的 lab 文件。 - 接着使用
git merge origin/check1-startercode下载 Lab 1 的代码文件。 - 确保你的环境已经正确搭建好:
cmake -S . -B build - 编译源代码:
cmake --build build - 开始 Lab 1 的挑战!
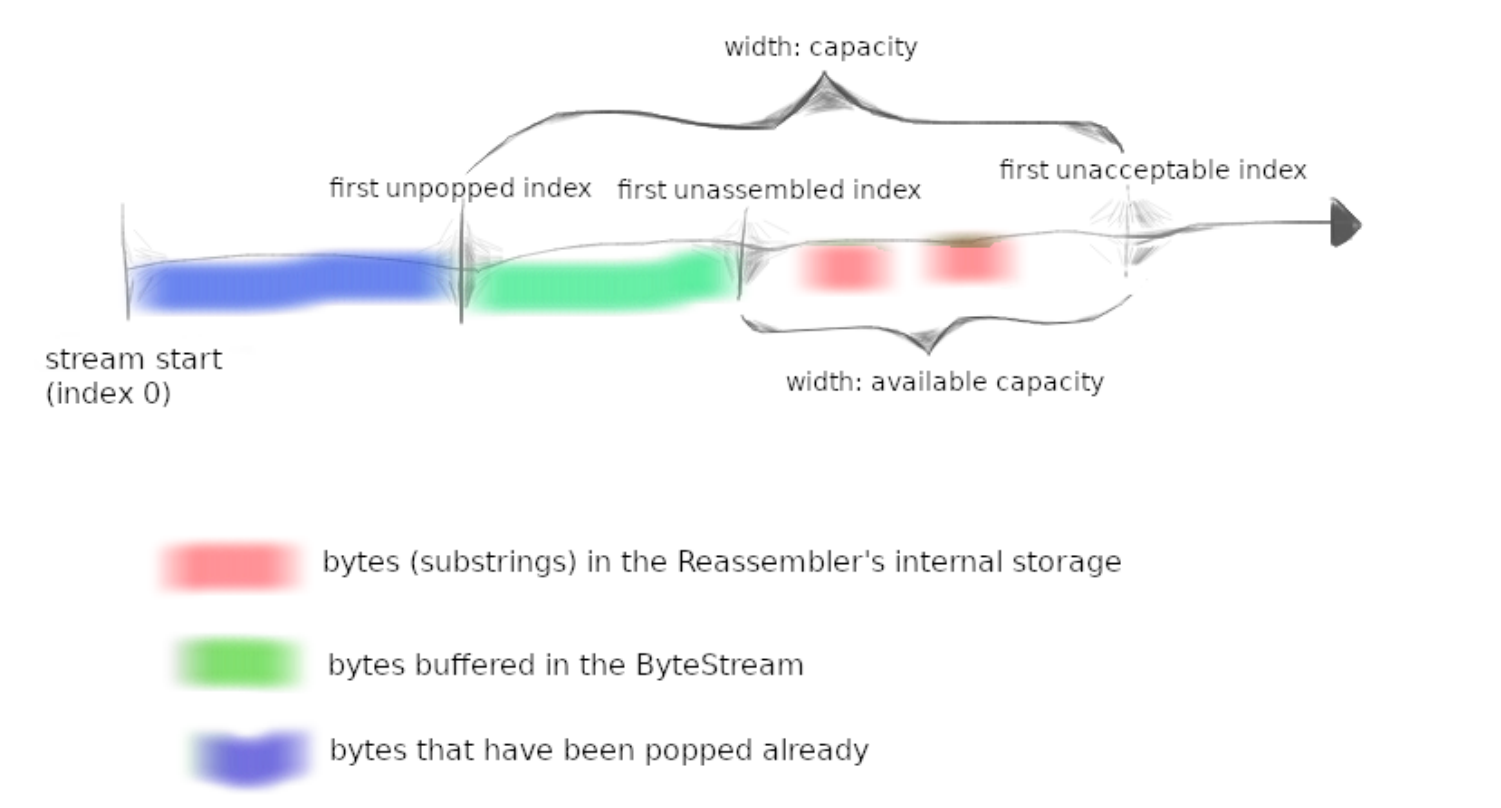
Putting substrings in sequence
在这个 Lab 和下一个 Lab 中,我们将实现 TCP 的 receiver 模块。对于 TCP 的 sender 模块,它将应用的 byte stream 拆分成一个个较短的 segments(长度不大于 1460 bytes 的子串),然后传递给 Network 层。但是 Network 层可能将这些 segments 丢弃、重复传送、打乱顺序,因此在 receiver 模块中,我们需要实现一个 Reassembler ,将这些 segments 重新组装成最初的 byte stream 。
What should the Reassembler store internally?
Reassembler 需要解决 3 种问题:
- 立即将要 push 的下一个 bytes 传送给
Writer。 - 将在 available capability 以内但是暂时还没轮到它传送的 bytes 存储在 buffer 中。
- 超过 available capability 的 bytes 直接丢弃。
在实现 Reassembler 时的一个重要原则就是要限制内存的使用量。
FAQs
详见 lab_faq
Development
最大的一个难点就是如何去除重复的子串,其余部分主要还是注意要求和细节如何模拟。
首先,这些 substrings 既是有序的又会出现重复,很容易想到使用 set 来存储,但是 set 的插入是 的,在 reassembler_win 这个样例中会超时。
于是我们考虑使用 map 来存储,每次存入一个 substring 时都遍历一遍 map 将重复的部分去除,然后再把删减后的 string 插入 map 中即可。
这里要注意一个细节,在遍历 map 的过程中,有一种容易忽略的情况就是当前遍历得到的 string 是要插入的 string 的 substring ,这时候需要将两头非重复部分的 substring 分别插入 map 。
Outcome
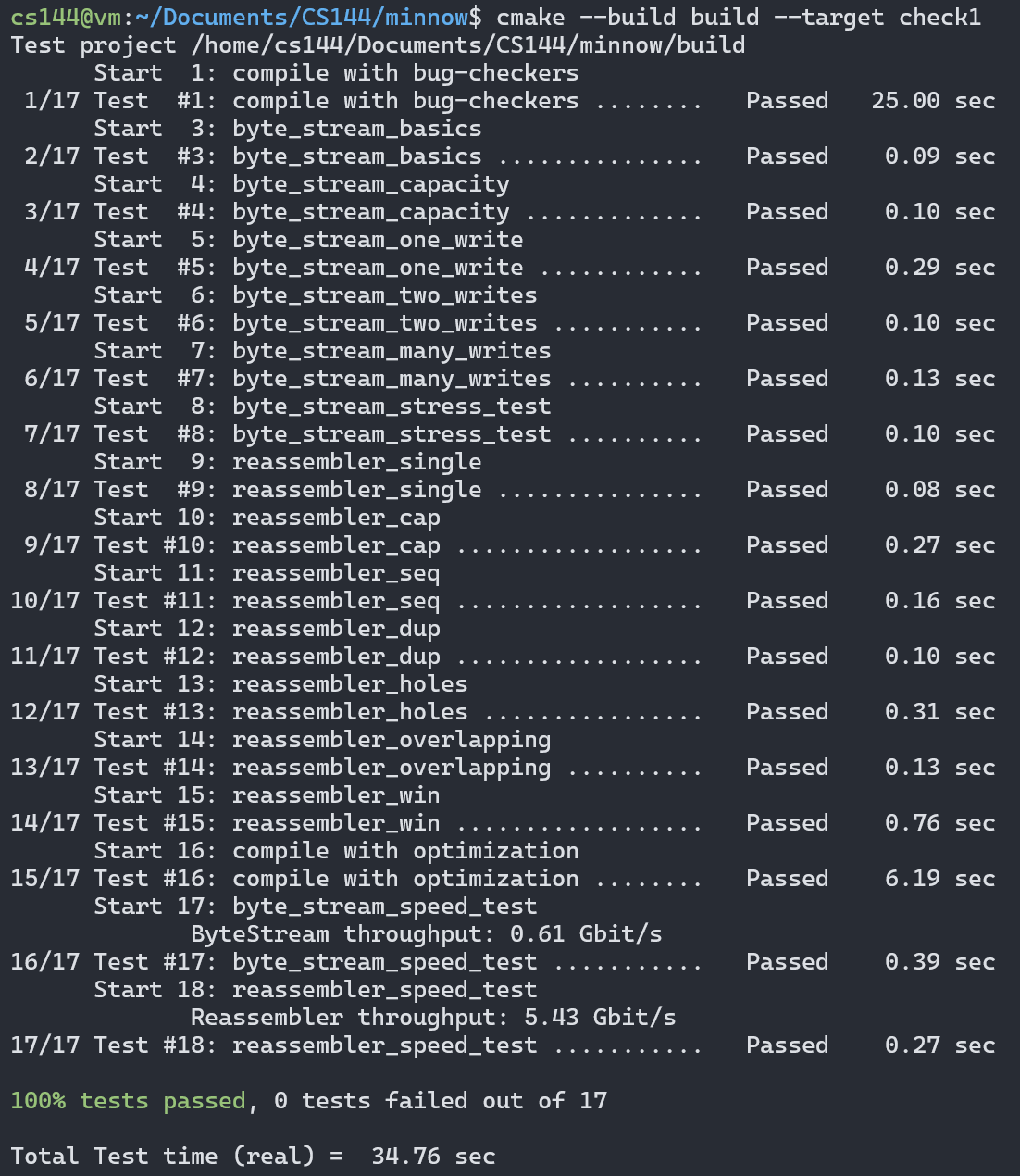
ByteStream throughput: 0.61 Gbit/s
Reassembler throughput: 5.43 Gbit/s
不算快也不算慢吧…
Source Code
reassembler.hh:
class Reassembler
{
private:
std::map < uint64_t, std::string > buffer_ {};
uint64_t first_index_in_buffer { 0 };
uint64_t buffer_size_ { 0 };
bool has_last_substring { 0 };
uint64_t first_unassembled_index { 0 };
void insert_into_buffer( uint64_t first_index, std::string data, bool is_last_substring );
void insert_from_buffer( Writer& ouput );
};reassembler.cc:
#include "reassembler.hh"
using namespace std;
void Reassembler::insert( uint64_t first_index, string data, bool is_last_substring, Writer& output )
{
// Your code here.
(void)first_index;
(void)data;
(void)is_last_substring;
(void)output;
if (data.empty()) {
if (is_last_substring) output.close();
return;
}
if (output.available_capacity() == 0) return;
uint64_t last_index = first_index + data.size();
uint64_t first_unacceptable_index = first_unassembled_index + output.available_capacity();
if (first_index >= first_unacceptable_index || last_index <= first_unassembled_index) return;
if (last_index > first_unacceptable_index) {
data = data.substr(0, first_unacceptable_index - first_index);
is_last_substring = false;
}
if (first_index < first_unassembled_index) {
data = data.substr(first_unassembled_index - first_index);
first_index = first_unassembled_index;
} else if (first_index > first_unassembled_index) {
insert_into_buffer(first_index, data, is_last_substring);
return;
}
first_unassembled_index += data.size();
output.push(move(data));
if (is_last_substring) { output.close(); return; }
if (!buffer_.empty() && buffer_.begin()->first <= first_unassembled_index) insert_from_buffer(output);
}
void Reassembler::insert_into_buffer( uint64_t first_index, string data, bool is_last_substring ) {
uint64_t l = first_index, r = first_index + data.size();
for (auto it = buffer_.begin(); it != buffer_.end() && l < r; ) {
if (it->first <= l) {
l = max(l, it->first + it->second.size());
++it;
continue;
}
if (l == first_index && r <= it->first) {
buffer_[l] = move(data);
buffer_size_ += data.size();
if (is_last_substring) has_last_substring = 1;
return;
}
uint64_t rr = min(r, it->first);
buffer_[l] = data.substr(l - first_index, rr - l);
buffer_size_ += rr - l, l = rr;
}
if (l < r) {
buffer_size_ += r - l;
buffer_[l] = data.substr(l - first_index);
}
if (is_last_substring) has_last_substring = 1;
}
void Reassembler::insert_from_buffer( Writer& output ) {
for (auto it = buffer_.begin(); it != buffer_.end(); ) {
if (it->first > first_unassembled_index) break;
uint64_t l = it->first, r = l + it->second.size();
if (r <= first_unassembled_index) {
buffer_size_ -= it->second.size();
} else {
string data = move(it->second);
buffer_size_ -= data.size();
data = data.substr(first_unassembled_index - it->first);
first_unassembled_index += data.size();
output.push(move(data));
}
it = buffer_.erase(it);
}
if (buffer_.empty() && has_last_substring) output.close();
}
uint64_t Reassembler::bytes_pending() const
{
// Your code here.
return buffer_size_;
}